alkene to alkyne mechanism – dissolving metal reduction alkyne
alkene to alkyne mechanism
8,9: E2 Reactions and Alkyne Synthesis
· Alkene and Alkyne Chemistry, Mark G, Moloney, Fellow and Tutor in Chemistry at St Peter’s College and Professor of Chemistry, University of Oxford, UK, Search for more papers by this author, Mark G, Moloney, Fellow and Tutor in Chemistry at St Peter’s College and Professor of Chemistry, University of Oxford, UK , Search for more papers by this author, Mark G, Moloney, Fellow and Tutor in
Alkyne Reduction by Lindlar’s Catalyst or Na/NH3
mechanism using HBr / ROOR / h for free radical addition to alkane pi bonds anti-Markovnikov addition = Br adds to less substituted position to form most stable free radical intermediate and then H adds to more substituted position H3C H2 C C H2 Br H3C H C CH2 HBr R2O2 cat h overall reaction 1, initiation two steps R O O R h R O O R H Br R O R O H Br
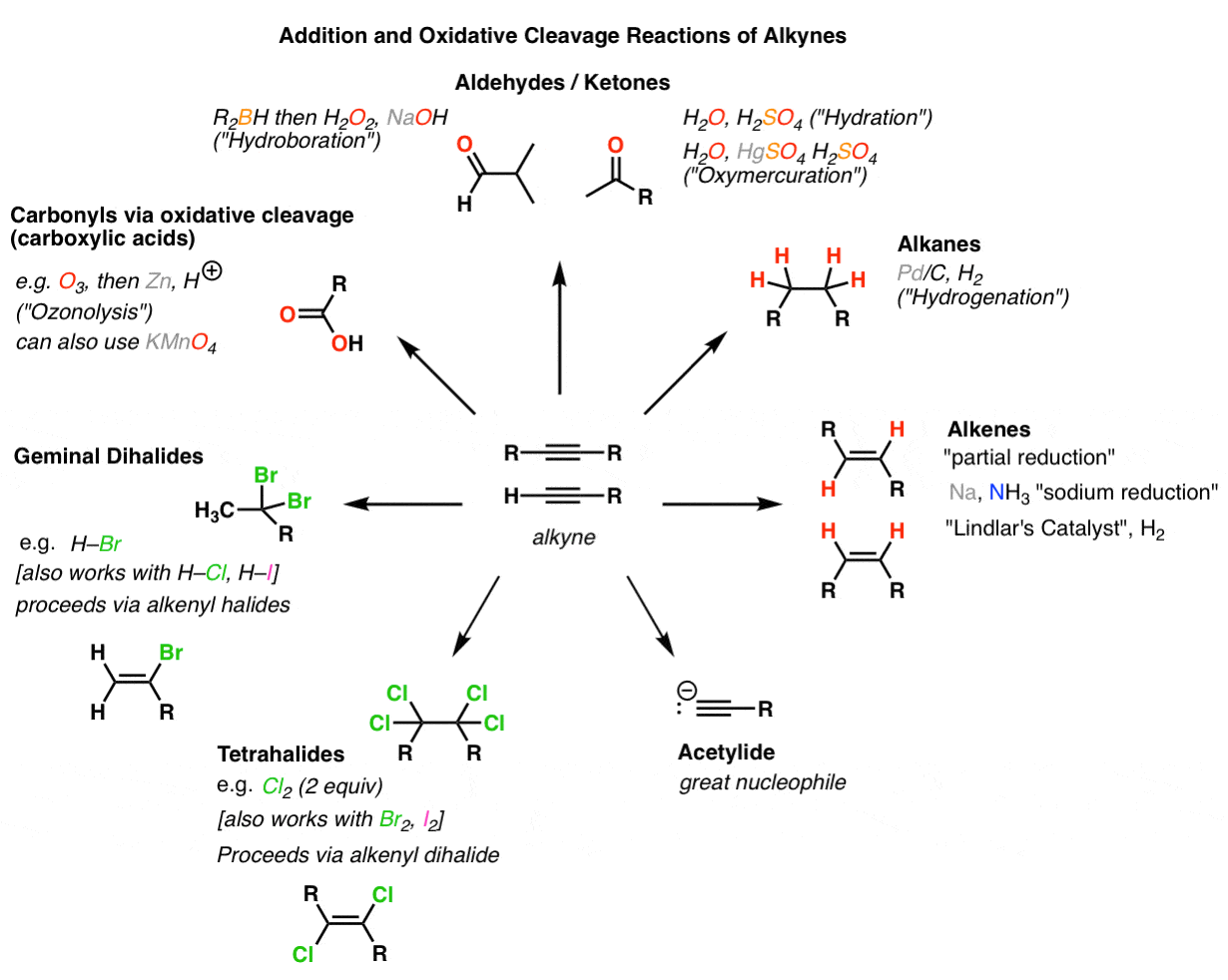
We have already seen a little earlier that alkynes can be partially reduced to give an alkene using the Lindlar’s catalyst That reaction gave us a cis-alkene But what if we need a trans-alkene? Well there’s a reaction that can accomplish just that! This reaction uses most commonly sodium metal Na as a reducing agent, You may also occasionally see lithium Li used in the same way, The mechanism of this reaction is rather …
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes Elimination Reactions
· Fichier PDF
alkene-forming eliminations Alkyne-forming elimination reactions are described in a subsequent section Common Features of Elimination Reactions 9,1A A variety of different types of substrates undergo elimination reactions to form alkenes but many of these reactions have common features General Equations We can represent elimination reactions that form alkenes with the following general
Ozonolysis
What Is Ozonolysis?
•Alkynes can also be reduced into trans alkene by an entirely different reaction called dissolving metal reduction, •Dissolving metal reduction – reduces an alkyne to a trans alkene using sodium metal and ammonia •This reaction is stereoselective for anti addition of H and H Dissolving Metal Reduction
Alkene and Alkyne Chemistry
Alkene formation in E1 reactions is not stereospecific After the leaving group leaves there is time for rotation about the Cα-Cβ bond to occur in the intermediate carbocation before ethanol acting as a base removes a β-H from that carbocation, As a result, the alkene product is a mixture of …
Taille du fichier : 2MB
9,5: Reduction of Alkynes
So what about the case where carbon has a double alkene or triple alkyne bond? You may already see the difficulty following the VSEPR model of attempting to bend another orbital around the carbon atom to form a second σ bond-such would bring electrons from different orbitals close to each other, increasing the energy of the system owing to strong repulsive forces,
Reactions of Alkynes — Organic Chemistry Tutor
The reaction starts by an electron transfer from lithium or sodium atoms to the triple bond of the alkyne forming a radical anion which deprotonates ammonia The resulting radical picks up another electron from the metal atom turning onto a carbanion which is again protonated by ammonia Check Also in Alkynes Introduction to Alkynes
Theoretical Calculations of Alkyne Metathesis Me Me R3M Me Me Me R3M R3M Me Me Me M = W R = OMe, NMe2 M = Mo R = OMe, CH2F Me Zhu, J,; Gia, J,; Lin, Z, Organometallics 2006, 25, 1812, • B3LYP level of Density Functional Theory, LanL2DZ basis set for W and Mo atoms , 6-31G basis set for C, N, F, O and H, MeO Mo MeO OMe MeO W MeO OMe Me W 2N Me2N NMe2 FCH Mo 2O
Properties Synthesis and Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
Alkyne Metathesis
· Fichier PDF
Alkenes To Alkynes Via Halogenation And Elimination Reactions
Alkynes from Alkenyl Halides: Elimination of A Vinyl Halide to Give An Alkyne
Chapter 9 Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes Elimination
· Fichier PDF
Chapter 9 Alkynes
· Fichier PDF
· Hydrogenation of an Alkyne to a E-Alkene trans-alkene Alkynes can be reduced to trans-alkenes with the use of sodium dissolved in an ammonia solvent, An Na radical donates an electron to one of the P bonds in a carbon-carbon triple bond, This forms an anion, which can be protonated by a hydrogen in an ammonia solvent,
This is a simple process using first halogenation of the alkene bond to form the dihaloalkane, and next, using the double elimination process to protonate the alkane and from the 2 Pi bonds, This first process is gone over in much greater detail in the page on halogenation of an alkene,
Organic Reactions Summary Alkenes alkynes and variations
· Fichier PDF