carboxypeptidase specificity – carboxypeptidase breaks down
The specificity of carboxypeptidase has now been reinvestigated by means of crystalline carboxypeptidase preparations obtained by the method of Anson 3 Some of the results of this investigation are reported in Table I It will be noted that the amount of enzyme required for the hydrolysis of a substrate varies widely with the nature of the substrate The carbobenzoxyglycyl derivatives of
Specificity of the Carboxypeptidase Inhibitor from Potatoes
· Carboxypeptidase T CpT EC 3,4,17,18 from Thermoactinomyces vulgaris an enzyme with only 30% and 27% amino acid sequence identity compared to CpA and CpB has nevertheless a similar three-dimensional structure and organization of the active center The S1′ subsite of CpT mainly differs from that of CpB by five substitutions CpB → CpT: Ser207 → Gly215 Gly243 → Ala251 Ala250 → Thr257, Gly253 → …
On the specificity of carboxypeptidase N a comparative
These mutants step-by-step reconstruct the primary specificity pocket of carboxypeptidase B CpB which is capable of cleaving only positively charged C-terminal residues All of the mutants retained the substrate specificity of the wild-type CpT Based on comparison of three-dimensional structures of CpB and the CpT5 model, it was suggested that the lower affinity of CpT5 for positively charged substrates than the affinity of …
Carboxypeptidase A
carboxypeptidase specificity
The Specificity of Carboxypeptidase
[PDF] The specificity of carboxypeptidase,
All the information hitherto available with respect to the specificity of carboxypeptidase has been obtained by the use of crude enzyme preparations 1, Consequently, there still remains some uncertainty as to whether the previously reported hydrolyses of various synthetic substrates, attributed to the action of carboxypeptidase, are all due to the same enzyme,
Carboxypeptidase
· Carboxypeptidase O CPO is a membrane-anchored brush-border enzyme associated with the small intestinal phase of protein digestion with distinctive specificity toward acidic C-terminal C-t amino acids The combined activity of human CPO hCPO and pancreatic carboxypeptidases enables the C-t proteolysis of the great majority of amino acids present in dietary proteins, Here we disclose mechanism …
Characterization of a digestive carboxypeptidase from the
Some carboxypeptidase A enzymes may differ slightly in specificity from mammalian enzymes due to differing active site residues see below, Similarly, a carboxypeptidase B has been identified in bollworm Lepidoptera; Helicoverpa armigera that is highly specific for C-terminal Lys residues [11], The insect glutamate carboxypeptidase has a high degree of specificity towards C-terminal Glu residues, It cleaves the synthetic …
Carboxypeptidase O is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol
A carboxypeptidase EC number 3,4,16 – 3,4,18 is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes cleaves a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal C-terminal end of a protein or peptide, This is in contrast to an aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at the N-terminus of proteins, Humans, animals, bacteria and plants contain several types of carboxypeptidases that have diverse functions ranging from catabolism to protein maturation,
Manquant :
specificity
Crystal structure and mechanism of human carboxypeptidase
Carboxypeptidase A – an overview
The structure of the enzymatically active subunit of human plasma carboxypeptidase N was modeled based on the homology with bovine carboxypeptidase A The active site of carboxypeptidase N is well conserved in comparison with carboxypeptidase A From a comparison of energetically favorable binding sites for different atomic probe groups a hypothesis for the differences in substrate specificity
In the pancreatic carboxypeptidases, this specificity is imparted by residue 255, which is an Asp in CPB and a Leu or Iie in CPA 56, 57 , However, the amino acid in a linearly similar position in CPD-2 as well as in most other members of the regulatory carboxypeptidase subfamily is Gln-257 132 ,
· Carboxypeptidase O is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored intestinal peptidase with acidic amino acid specificity Lyons PJ 1 Fricker LD 1Department of Molecular Pharmacology Albert Einstein College of Medicine Bronx New York 10461, USA,
Structural principles of the wide substrate specificity of
Carboxypeptidase – an overview
· Carboxypeptidase B is highly specific for basic C-terminal residues with arginine favoured over lysine [] Specificity is primarily determined by interaction of the side chain of the C-terminal amino acid of the substrate with a binding pocket on the enzyme with amino acid 255 human carboxypeptidase A1 numbering at the bottom [] The side chain of this residue interacts with the substrate side chain; in carboxypeptidase B …
Structural insights into the broad substrate specificity
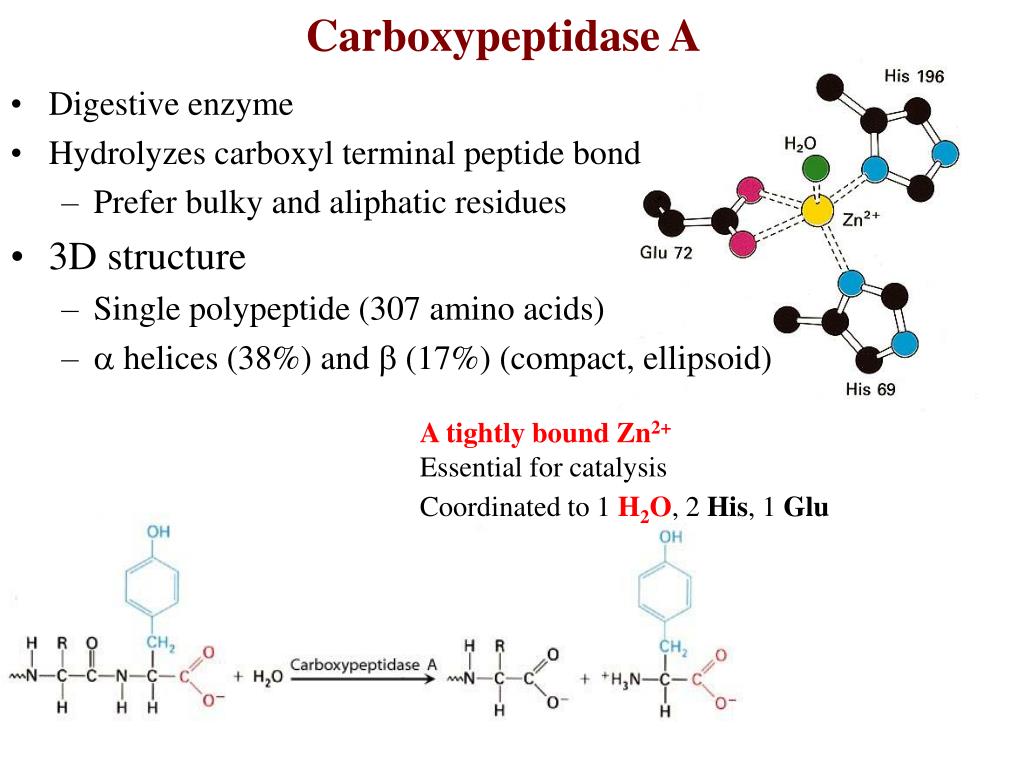
Classified as a metalloexopeptidase, carboxypeptidase A consists of a single polypeptide chain bound to a zinc ion, This characteristic metal ion is located within the active site of the enzyme, along with five amino acid residues that are involved in substrate binding: Arg-71, Arg-127, Asn-144, Arg-145, Tyr-248, and Glu-270, X-ray crystallographic studies have revealed five subsites on the protein, These allosteric sites are involved in creating the ligand-enzyme specificity …
Carboxypeptidases from animal plant fungal and bacterial sources were tested for their ability to bind to the carboxypeptidase inhibitor from Russet Burbank potatoes Enzymes which participate in the degradation of dietary protein were partially purified from animal species as diverse as the cow and the limpet and all were potently affected by the inhibitor However, several zymogens of the enzymes in this group were tested and …
Cited by : 3