concentration formula chem – how to calculate concentrations
· More Ways to Calculate and Express Concentration , There are other easy ways to express the concentration of a chemical solution, Parts per million and parts per billion are used primarily for extremely dilute solutions, g/L = grams per liter = mass of solute / volume of solution F = formality = formula weight units per liter of solution
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 7 mins
Concentration of Solution
Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
Comment calculer la concentration d’une solution En chimie la concentration d’une solution est la quantité de matière soluble aussi appelée soluté dissoute dans une autre matière dissolvante aussi appelée solvant La formule classique
Molarity Concentration of Solutions Calculations Chemistry
How to Calculate Concentration
The formula is as follows: In case of mass we may express it as: Mass of solute/Mass of solution × 106 In case of volume we may express it as: Volume of solute/Volume of solution × 106 So we can express the concentration of solutions in parts per million as mass to mass, volume to volume and mass to volume form,
Solution Concentration
concentration formula chem
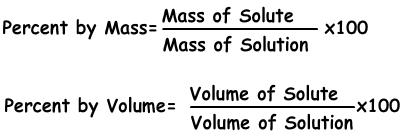
Or using formula; Percent by mass=10,100/80=12,5 % Example: If concentration by mass of 600 g NaCl solution is 40 %, find amount of solute by mass in this solution,
In chemistry, concentration of a solution is often measured in molarity M, which is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, This molar concentration c i is calculated by dividing the moles of solute n i by the total volume V of the: [latex]\text{c}_\text{i}=\frac{\text{n}_\text{i}}{\text{V}}[/latex]
Expressing Concentration of Solutions: Methods Formulas
· In chemistry a solution’s concentration is how much of a dissolvable substance known as a solute is mixed with another substance called the solvent The standard formula is C = m/V where C is the concentration, m is the mass of the
Vues : 1,6 M
Concentration Units
Concentration with Examples
Usually one wants to keep track of the amount of the solute dissolved in the solution We call this the concentrations One could do by keeping track of the concentration by determining the mass of each component but it is usually easier to measure liquids by volume instead of mass, To do this measure called molarity is commonly used, Molarity M is defined as the number of moles of solute n divided by the …
5 Easy Ways to Calculate the Concentration of a Solution
· Ka = [H3O +][A −] [HA] The concentration of the hydrogen ion [H +] is often used synonymously with the hydrated hydronium ion [H3O +] , To find a concentration of hydronium ions in solution from a pH, we use the formula: [H3O +] = 10 − pH, This can be flipped to calculate pH from hydronium concentration:
Chapter 4: Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry
· Fichier PDF
· v/v % = [ volume of solute/ volume of solution] x 100% Note that volume percent is relative to the volume of the solution not the volume of solvent For example wine is about 12% v/v ethanol This means there is 12 ml ethanol for every 100 ml of wine
The concentration of solution formula is given as follows, Cor S = \[\frac{\text{Weight of solute in grams}}{\text{Volume in litres}}\] We will also see other methods on how to calculate concentration of a solution based on the different methods of expressing concentrations,
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 5 mins
Calculating Concentrations with Units and Dilutions
· A concentration expressed on an m/m basis is equal to the number of grams of solute per gram of solution; a concentration on an m/v basis is the number of grams of solute per milliliter of solution, Each measurement can be expressed as a percentage by multiplying the ratio by 100; the result is reported as percent m/m or percent m/v, The concentrations of very dilute solutions are often expressed in
3 manières de calculer la concentration d’une solution
4,5: Concentration of Solutions
c HCl = 001 mol L -1 c stands for concentration formula given in round brackets or parentheses Equation formula or expression to calculate the molarity of a solution concentration in mol L -1 is c = n ÷ V,
terms: amount concentration mass concentration volume concentration and number concentration Molar concentration molar analytical concentration and molar equilibrium concentration are all amount concentrations by this definition, The molar analytical concentration of H 2 SO 4 is given by cH 2 SO 4 = [SO 4-2] + [HSO 4 2] because -SO