define law of segregation – anti segregation laws
define law of segregation
Define law of segregation?
Law A body of rules of conduct of binding legal force and effect prescribed recognized and enforced by controlling authority In US, law, the word law refers to any rule that if broken subjects a party to criminal punishment or civil liability, Laws in the United States are made by federal, state, and local legislatures, judges, the president, state governors, and administrative agencies,
Law of Segregation and Law of Dominance
Define Law Of Segregation
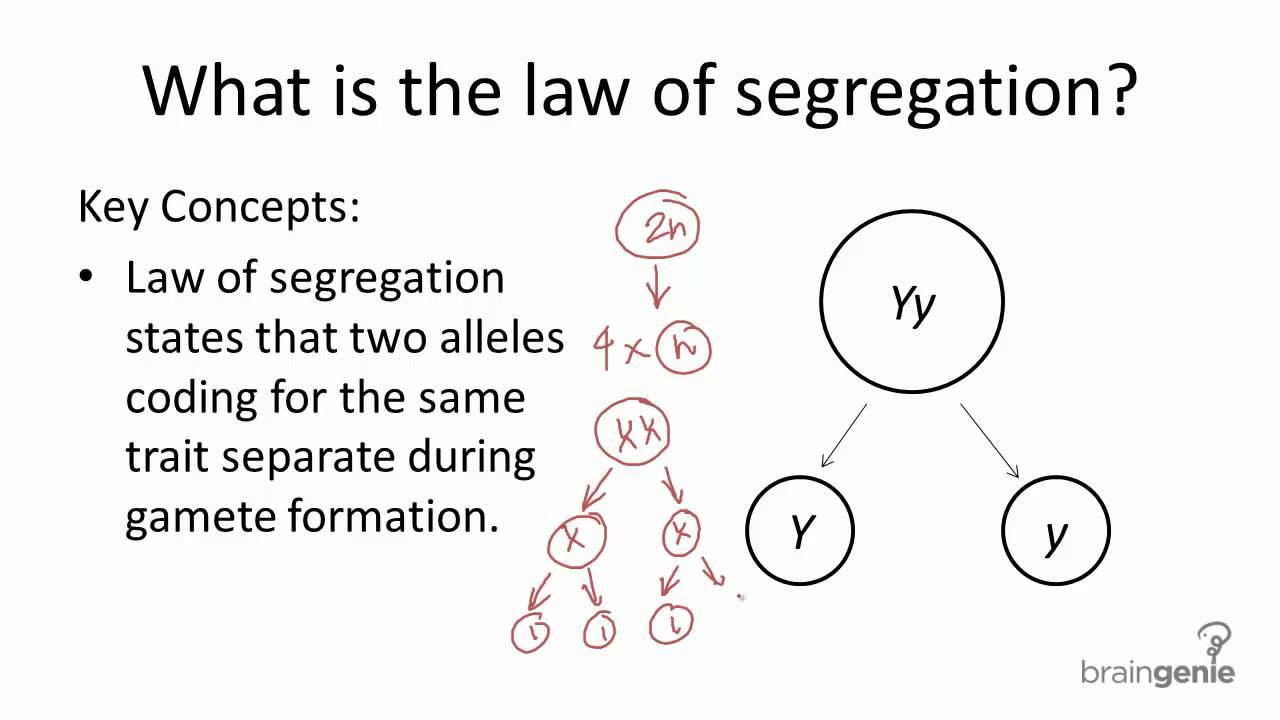
The law of segregation states that each individual that is a diploid has a pair of alleles copy for a particular trait, Each parent passes an allele at random to their offspring resulting in a diploid organism, The allele that contains the dominant trait determines the phenotype of the offspring, In essence, the law states that copies of genes separate or segregate so that each gamete receives only one allele,
“Law of segregation,” Merriam-Webster,com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www,merriam-webster,com/dictionary/law%20of%20segregation, Accessed 25 Aug, 2021,
Law of segregation legal definition of law of segregation
Law of segregation Definition & Meaning
Define the law of segregation?
12,3C: Mendel’s Law of Segregation
What Is Mendel’s Law of Segregation?
· Law of Segregation Definition, Gregor Mendel’s law of segregation states that the two alleles for each trait segregate, or separate, during the formation of gametes, and that during the formation of new zygotes, the alleles will combine at random with other alleles, The law of segregation ensures that a parent, with two copies of each gene, can pass on either allele,
Law of Segregation
Find an answer to your question Define Law Of Segregation PRATHAMABD PRATHAMABD 07,01,2020 English Secondary School answered • expert verified Define Law Of Segregation 2 See answers
Law of segregation
· Updated November 27, 2019, The principles that govern heredity were discovered by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s, One of these principles, now called Mendel’s Law of Segregation, states that allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation and randomly unite at fertilization ,
What is law of segregation explain with example
Law of segregation: This law states that when a pair of contrasting factors or genes are brought together in a heterozygote hybrid, the two members of the allelic pair remain together without being contaminated and when the gametes are formed from the hybrid and the two separate out …
Law Of Segregation
· Law of segregation: Alleles or genes remain together and segregate at the time of gamete formation, This means that the alleles do not mix in the hybrids Non-mixing of alleles, This is also known as law of purity of gametes,
Men′del’s law′ 1, Also called law of segregation, the principle stating that during the production of gametes the two copies of each 2, Also called law of independent assortment, the principle stating that the laws of chance govern which particular 3, Also called law of dominance, the
· Three Different Mendel inheritance laws are as follows: Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment Law of Dominance
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 10 mins
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
· Also called law of segregation the principle stating that during the production of gametes the two copies of each hereditary factor segregate so that offspring acquire one factor from each parent 2 Also called law of independent assortment,
The Law: 1, The Law of Segregation: The law states that when any individual produces gametes, the copies of a gene separate so that each gamete receives only one copy, Either of the alleles will be received by the gamete, 2, The Law of Dominance: If there are two alleles coding for the same trait and one is dominant it will show up in the organism while the other won’t,
Law of segregation definition, the principle, originated by Gregor Mendel, stating that during the production of gametes the two copies of each hereditary factor segregate so that offspring acquire one factor from each parent, See more,