einstein de sitter model – einstein de sitter universe
einstein de sitter model
· The Einstein de Sitter model is just a special case of the more general result, EdS universe represents a matter-dominated universe, Since the universe evolving towards lambda dominated and recently it was matter dominated, its a good approximation to use the EdS model to calculate the age of the universe,
Einstein-De Sitter debate
· Fichier PDF
Einstein–de Sitter space was the favorite model for an expanding universe until the 1980s, After the inflation theory was proposed, vacuum energy or dark energy had to be considered, This can be represented by a cosmological constant , which Einstein inserted into his theory of general relativity to achieve a …
Univers de de Sitter — Wikipédia
Einstein discussed with De Sitter also come up in Einstein’s correspondence in 1918 with the Ger-man physicist Gustav Mie 1868–1957, The picture that emerges is one of Einstein holding on with great tenacity to two beliefs con-cerning the universe that guided him in the construction of his cosmological model…
Après la découverte de l’expansion de l’Univers par Hubble, Einstein, qui était jusqu’alors sceptique au sujet des travaux de Friedmann et Lemaître sur des modèles cosmologiques non statiques, comprend leur valeur, Ainsi, au début des années 1930, il aide à répandre ces idées parmi les physiciens, En 1932, lui-même et De Sitter proposent un modèle cosmologique minimal
Can the Einstein-de Sitter model adequately describe the
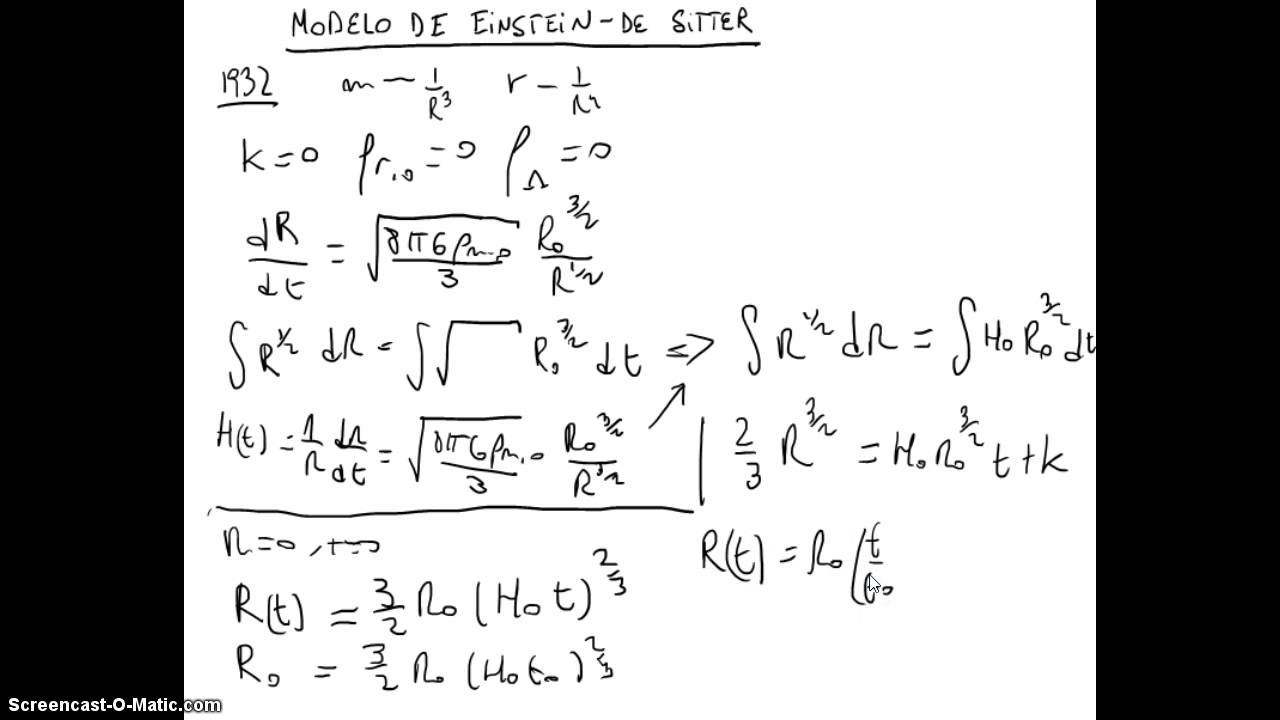
Other articles where Einstein-de Sitter model is discussed: cosmology: The Einstein–de Sitter universe: In 1932 Einstein and de Sitter proposed that the cosmological constant should be set equal to zero, and they derived a homogeneous and isotropic model that provides the separating case between the closed and open Friedmann models; i,e,, Einstein and de Sitter…
A cosmological model not to be confused with the de Sitter cosmological model which assumes a homogeneous isotropic constant curvature universe with zero cosmological constant \Lambda and pressure P \Lambda = P = r_0^{-2}\equiv 0 See also: Cosmology de Sitter Cosmological Model Einstein …
Espace d’Einstein-de Sitter — Wikipédia
Vue d’ensemble
Einstein–de Sitter universe
Overview
Einstein-de Sitter Cosmological Model — from Eric
Einstein-de Sitter model
L’ univers Einstein-de Sitter est un modèle de l’univers proposé par Albert Einstein et Willem de Sitter en 1932, En apprenant pour la première fois la découverte par Edwin Hubble d’une relation linéaire entre le décalage vers le rouge des galaxies et leur distance, Einstein a défini l’ univers cosmologique constante à zéro dans les équations de Friedmann, résultant en un modèle de
The Einstein–de Sitter universe, In 1932 Einstein and de Sitter proposed that the cosmological constant should be set equal to zero, and they derived a homogeneous and isotropic model that provides the separating case between the closed and open Friedmann models; i,e,, Einstein and de Sitter assumed that the spatial curvature of the universe is neither positive nor negative but rather zero,
See also: Einstein-de Sitter Cosmological Model Astrophysics: Cosmology: de Sitter Cosmological Model : A static cosmological model made isotropic and homogeneous by removing all mass from the universe The resulting expanding universe had density of zero and constant curvature In this model, the radius as a function of time is given by where H is the Hubble constant, equal to where is the
The characteristics of Friedmann model universes containing decoupled matter and radiation are investigated to establish the range in redshift over which the frequently assumed Einstein-de Sitter approximation is valid This approximation is found to have decidedly doubtful value for small yet entirely plausible values of the material density parameter,
cosmology – The Einstein–de Sitter universe
cosmology
Nouveaux modèles cosmologique
Univers Einstein–de Sitter
En cosmologie l’univers de de Sitter en anglais : de Sitter Universe est un modèle cosmologique dans lequel la seule contribution à la densité d’énergie provient de la constante cosmologique [1] C’est une solution exacte des équations de la relativité générale correspondant physiquement à un univers homogène isotrope, vide de matière mais rempli d’une constante cosmologique
de Sitter Cosmological Model — from Eric Weisstein’s
Cosmology of Einstein-de Sitter Universe