linux swap memory – free swap memory linux
Just as Linux uses free memory for purposes such as buffering data from disk, there eventually is a need to free up private or anonymous pages used by a process, These pages, unlike those backed by a file on disk, cannot be simply discarded to be read in later, Instead they have to be carefully copied to backing storage, sometimes called the swap area, This chapter details how Linux uses and
8 Useful Commands to Monitor Swap Space Usage in Linux
· 8 Commands to Check Linux Swap Space Usage Therefore in this article we are going to look at ways to monitor swap space usage in a Linux systems What is Swap space? Swap space is a restricted amount of physical memory that is allocated for use by the operating system when available memory has been fully utilized It is memory management that involves swapping sections of memory to and from
The Linux free command Command: $ free This command is used to check memory and swap utilization on your system in a few lines Without the use of any switch the displayed output is printed in kilobytes Command: $ free -h With the -h switch, the free command displays the memory and swap utilization in …
How To Check Swap Usage Size and Utilization in Linux
· What is Swap Space in Linux? Swap which you may know as the paging file or page file on Windows is space set aside by the operating system to temporarily hold information that it can’t hold in RAM Rather than throw up errors and force you to close other applications Ubuntu “swaps” some of the information that’s in memory to a hard drive for later use This is not ideal – there’s a reason
What’s the right amount of swap space for a modern Linux
All about Linux swap space
· Fig01: Linux: Swap Memory Usage Command Sample outputs from glances command: Linux Find Out What Process Are Using Swap Space Try smem command: smem OR top Linux GUI tool to monitor swap space size and usage Try Gnome or KDE system monitor tool For example, the GNOME System Monitor shows you what programs are running and how much processor time, memory including paging/swap …
How to clear swap memory in Linux
Le swap est une mémoire physique “virtuelle”, souvent installée sous Linux dans une partition indépendante, Une partie du disque dur est réservée à cette mémoire virtuelle qui viendra soulager le système en cas de surcharge, La partition a un type bien spécifique, que l’on peut voir en lançant la commande fdisk,
5 Commands to Check Swap space in Linux – VITUX
· To clear the swap memory on your system, you simply need to cycle off the swap, This moves all data from swap memory back into RAM, It also means that you need to be sure you have the RAM to support this operation, An easy way to do this is to run ‘free -m’ to see what is being used in swap and in RAM, Once you power it off, you can wait an arbitrary amount of time 30 sec or so to give the
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 3 mins
linux swap memory
How Does Swap Memory in Linux Work?
What is Swap Memory in Linux?
· Our latest Linux articles Many years ago the rule of thumb for the amount of swap space that should be allocated was 2X the amount of RAM installed in the computer Of course that was when a typical computer’s RAM was measured in KB or MB So if a computer had 64KB of RAM a swap partition of 128KB would be an optimum size
Linux Find Out What Process Are Using Swap Space
Swap Management
Swap: Comment activer la mémoire d’échange sous Linux
Avantages et inconvénients de Swap
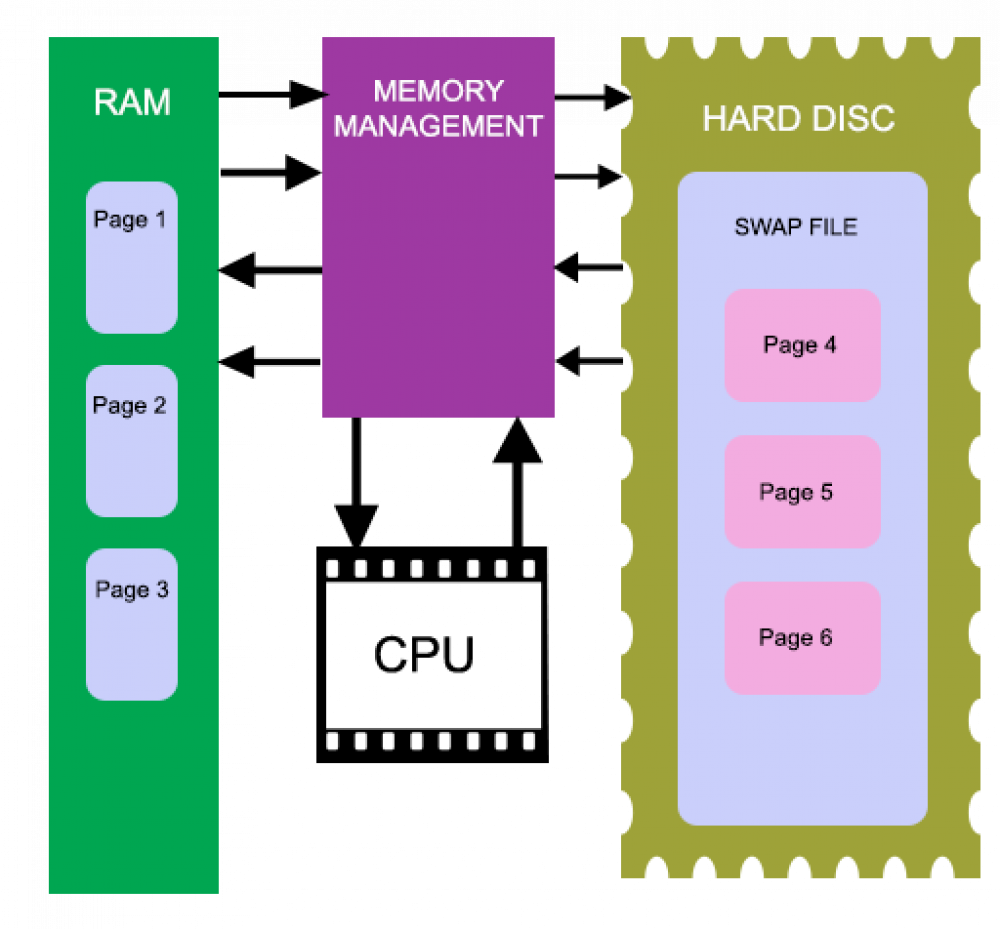
As explained above swap memory is the dedicated amount of hard drive that is used whenever RAM runs out of memory There is a memory management program in Linux that takes care of this process Whenever RAM is short of memory, the memory management program looks for all those inactive blocks of data present in RAM that have not been used for a long time,
Swap memory in Linux is used to prevent data overflow in RAM in event of the system facing high load, This helps prevent the system to become unresponsive due to a lack of memory, It also ensures that applications or processes don’t encounter ‘out-of-memory’ errors, How does swap memory work? In terms of memory, a page is a fixed block of memory space, The data blocks occupying the RAM
[Linux] Gestion de la RAM et du Swap
· The top command fakes this information by making SWAP = VIRT – RES, but that is not a good metric, because other stuff such as video memory counts on VIRT as well for example: top says my X process is using 81M of swap, but it also reports my system as a whole is using only 2M of swap, Therefore, I will not add a similar Swap column to htop because I don’t know a reliable way to get this
How to Create and Adjust Swap Space in Ubuntu 2004
· Linux divides its physical RAM random access memory into chucks of memory called pages, Swapping is the process whereby a page of memory is copied to the preconfigured space on the hard disk, called swap space, to free up that page of memory, The combined sizes of the physical memory and the swap space is the amount of virtual memory available,