pka of water – bordwell pka table
Bordwell pKa Table
· pKa is an acid dissociation constant used to describe the acidity of a particular molecule, Its value is directly related to the structure of the given compound, The constant changes depending on the solvent the compound is used in, Typically, organic chemists compare the various values from their determination in water, DMSO and the gas phase and use these to predict a compounds reactivity, solubility, and other physical characteristics, More information on pKa’s …
pka of water
pKa Data Compiled by R, Williams ACIDS Compound pK Ref, H3PO2 2,0, 2,23* 28 H2PO4– 7,21* 77 AgOH 3,96 4 HPO4_ 12,32* 77 AlOH3 11,2 28 AsOH H3PO3 2,0 28 3 9,22 28 H3AsO4 2,22, 7,0, 13,0 28 H2PO3– 6,58* 77 H H4P2O7 1,52* 77 2AsO4– 6,98* 77 HAsO4* 11,53* 77 H3 P2O7– 2,36* 77 As2O3 0 4 H2P2O7= 6,60* 77 H3AsO3 9,22* HP2O7= 9,25* 77
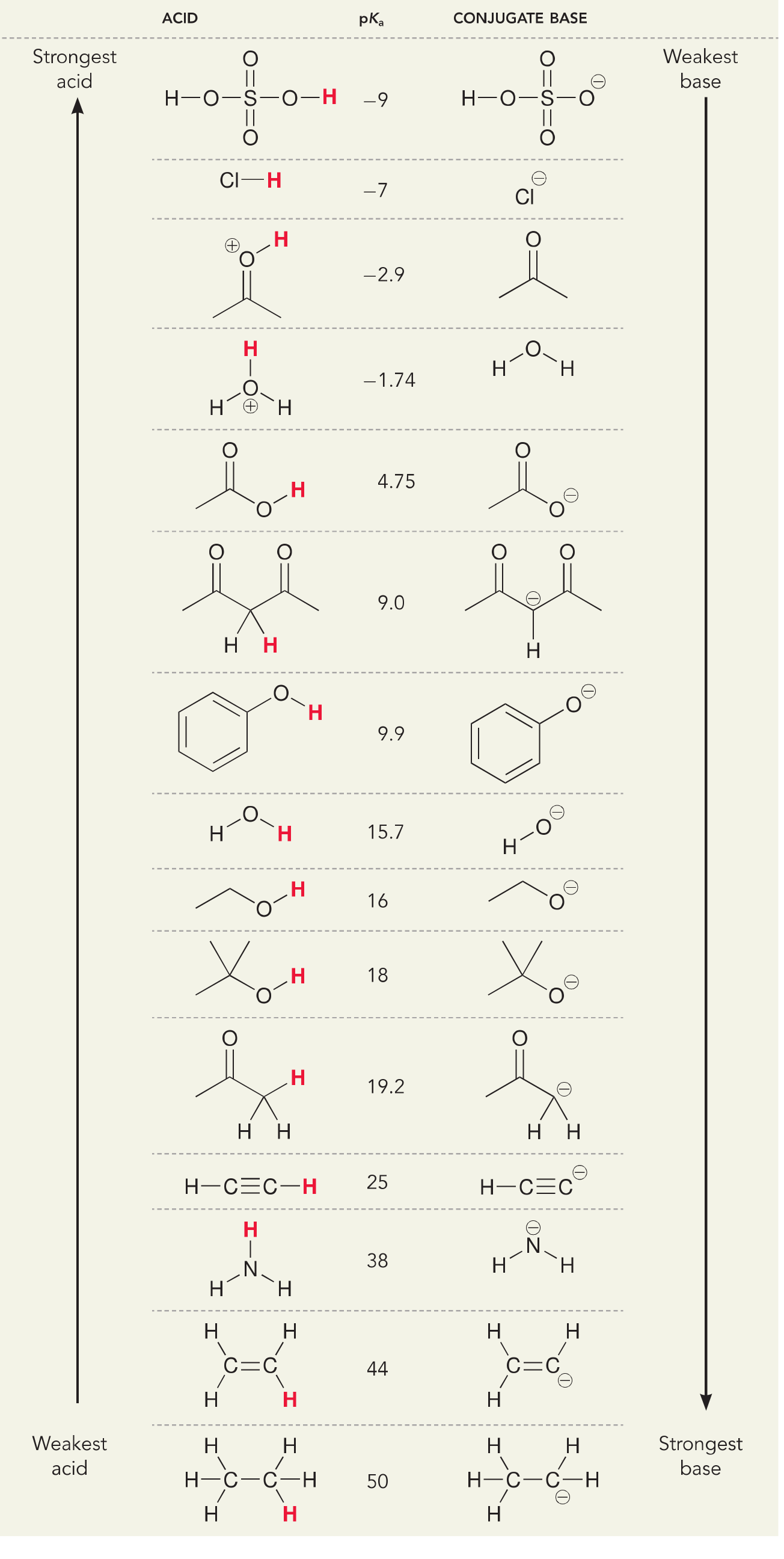
· You remember from introductory chemistry and life in general that the pH of pure water is 7, This derives from the general formulas for both pH and a new quantity, pKa, \[pH = -log[H_3O^+] = -log10^{-7} = 7\] \[pK_a = -logK_a = -log10^{-14} = 14\] Note: some books use 15,7 for the pKa of water, Here is a link to an explanation of why 14 is better,
· Therefore, the pH is the negative logarithm of the molarity of H, the pOH is the negative logarithm of the molarity of OH −, and the pKw is the negative logarithm of the constant of water: pH = − log[H +] pOH = − log[OH −] pKw = − log[Kw] At room temperature, Kw = 1,0 × 10 − 14, So, pKw = − log[1,0 × 10 − 14] = 14,
4, Ammonium ion pKa = 9‐10 5, Phenol pKa = 10 6, Thiol pKa = 10 7, Alcohol pKa = 16‐18 8, Water pKa = 15,7 9, Amide pKa = 18 10, Alpha proton of ketone/aldehyde pKa = 20 11, Alpha proton of ester pKa = 25 12, Terminal alkyne pKa = 25 13, Amine pKa = 38‐40 14,
2,2: Weak Acids and Bases, pH and pKa
· K a = [ A X −] [ H X +] [ H A] Thus in case of water, K a = [ O H X −] [ H X +] [ H X 2 O] The concentration of pure water at a temperature of 25 ∘ C is c = 55,345 m o l l − 1 , Therefore, K a = [ O H X −] [ H X +] [ H X 2 O] = 10 − 14 55,345 = 1,807 × 10 − 16 = 10 − 15,74, or, p K a = 15,74, Share,
Critiques : 5
physical chemistry
What is the pKa of water?
We find two types of silanol groups at the surface of quartz: out-of-plane silanols with a strong acidic character pKa = 56 which consequently results in the formation of strong and short hydrogen bonds with water molecules at the interface and in-plane silanols with a pKa of 8,5 forming weak hydrogen bonds with the interfacial water molecules Our estimate of the quartz point of zero charge 10 is found in good agreement …
Acid dissociation constant
pKa Values INDEX
· Fichier PDF
· What is the real pKa of water? 6, Why do most carboxylic acids have high pKa ~5 in spite of having a conjugate base ion that is stabilized by resonance? 2, Chalcogens’ hydrides as acids? 2, Which is a stronger acid: H3O+ or HCl? 1, At what pKa value do we consider an acid strong? 0, Acetone basicity , Related, 2, How many of different types of chemical species are in a certain volume of
Water has a very high specific heat capacity of 4184 J/kg·K at 25 °C – the second-highest among all the heteroatomic species after ammonia, as well as a high heat of vaporization 40,65 kJ/mol or 2257 kJ/kg at the normal boiling point, both of which are a result of the extensive hydrogen bonding between its molecules, These two unusual properties allow water to moderate Earth’s
K eq = a H 3 O + * a OH – / a H2O 2 [2] where a is the chemical activity of the water ions, Because most acid–base solutions are typically very dilute, the activity of water is generally approximated as being equal to unity, In dilute aqueous solutions, the activities of the solute particles are approximately equal to …
functional group pka
· Fichier PDF
Properties of water
In water, measurable pK a values range from about −2 for a strong acid to about 12 for a very weak acid or strong base, A buffer solution of a desired pH can be prepared as a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, In practice, the mixture can be created by dissolving the acid in water, and adding the requisite amount of strong acid or base,
Water
Water chemical formula: H2O is a transparent fluid which forms the world’s streams, lakes, oceans and rain, and is the major constituent of the fluids of organisms, As a chemical compound, a water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected by covalent bonds, Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature and pressure, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice; and gaseous state, steam water …
The Silica-Water Interface: How the Silanols Determine the
· In most general chemistry textbooks, the pK a of water at 25 ºC is listed as 14,0, In many organic chemistry textbooks and some biochemistry texts, however, the pKa of water at 25ºC is listed as 15,7, This module describes the derivation of these two values and describes why the value of 15,7 should not be used,
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 12 mins
physical chemistry
1,17: pka and pH
Water