pleural drain vs chest tube – pleural effusion chest tube drainage
Thoracocentesis and Chest Tubes
pleural drain vs chest tube
Having pleurodesis via a chest drain
· Fichier PDF
· Context Malignant pleural effusion causes disabling dyspnea in patients with a short life expectancyPalliation is achieved by fluid drainage but the most effective first-line method has not been determined Objective To determine whether indwelling pleural catheters IPCs are more effective than chest tube and talc slurry pleurodesis talc at relieving dyspnea,
Cited by : 530
Indwelling pleural catheters versus chest tube and talc
Context: Malignant pleural effusion causes disabling dyspnea in patients with a short life expectancy Palliation is achieved by fluid drainage but the most effective first-line method has not been determined Objective: To determine whether indwelling pleural catheters IPCs are more effective than chest tube and talc slurry pleurodesis talc at relieving dyspnea,
Cited by : 530
Chest Tube Drainage of the Pleural Space: A Concise Review
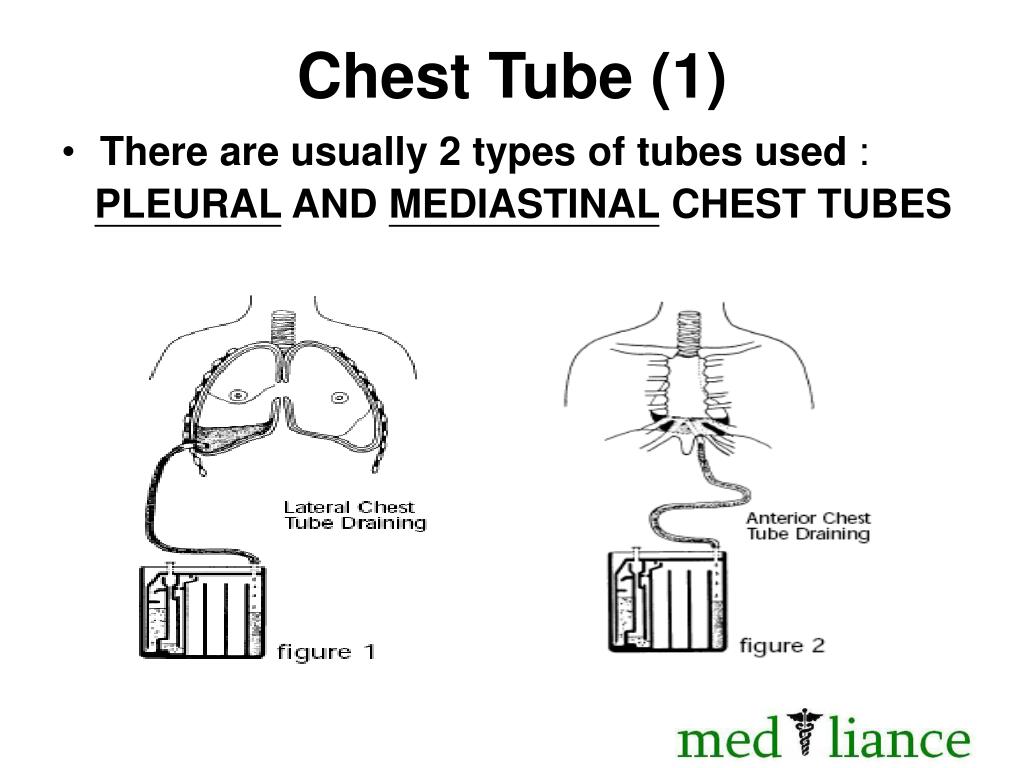
Chest Tube Pleural Drainage System
· There are two situations in which chest tubes are used in the management of malignant pleural effusions: i to facilitate a pleurodesis; and ii to drain the pleural fluid on a long-term basis with an indwelling chest tube 3 For pleurodesis large bore 24–32 F have been used in most studies involving sclerosing agents 4 Large bore rather than small bore 10–14 F were traditionally
Chest Tube Drainage of the Pleural Space: A Concise Review
All chest tubes are connected to a drainage system device: flutter valve underwater seal electronic systems or for indwelling pleural catheters IPC vacuum bottles The classic three-bottle drainage system requires either external wall suction or gravity “water seal” drainage the former not being routinely recommended unless the latter is not effective, The optimal timing for tube
Chest Tube Placement Thoracostomy and Pleurodesis
Chest tube placement is a minimally-invasive procedure small incisions of 2–3 inches long / local anesthesia performed to treat and prevent pleural effusions, Pleural effusion is a condition that causes excess fluid buildup in the lungs, specifically the pleura, The pleura is a thin membrane covering the surface of the lungs and chest wall, Some fluid is always found here, but the amount
· Chest tube placement also called tube thoracostomy is a common procedure in daily clinical practice which is performed to drain fluid blood or air from the pleural cavity It also serves as a route to instill antibiotics post-pneumonectomy empyemas sclerosing agents pleurodesis as well as fibrinolytics DNAse, and/or saline complicated parapneumonic effusions and empyemas, On the
Cited by : 27
Effect of an Indwelling Pleural Catheter vs Chest Tube and
Malignant pleural effusion causes dyspnoea in more than 1 million people annually and current guidelines recommend chest tube insertion and talc slurry as first-line treatment This unblinded randomised controlled trial aimed to determine whether indwelling pleural catheters IPCs are more effective at relieving dyspnoea in patients with malignant effusions than chest tube and talc pleurodesis,
Pleural controversy: Optimal chest tube size for drainage
LARGE PLEURAL EFFUSION CHEST TUBE MANAGEMENT Irina Kovatch MD Morbidity and Mortality Kings County Hospital Center June 24 th 2010 downstatesurgery,org PATIENT PRESENTATION 62 year old male with PMH of DM and HIV Admitted on 4/26/10 with symptoms x 2 weeks o, dysphagia, o, productive cough, o, shortness of breath, o, right-sided chest pain VS: T 97,9, BP 111/81, HR 103; WBC of 23 CT
Effect of an indwelling pleural catheter vs chest tube and
The tunneled pleural drainage catheter is similar to a kind of chest tube To allow regular drainage of pleural fluid at home a disposable bottle collection system is provided with the catheter A catheter is a long thin plastic tube that is considerably smaller than a “pencil lead” or approximately 1/8 inch in diameter The CT scanner is typically a large, donut-shaped machine with a short
Chest Tube and Pleurx
Chest tube: chest drain or thoracostomy tube; Thoracocentesis: pleural tap or pleurocentesis Definition Thoracocentesis refers to the procedure of puncture of the pleural cavity using a hollow needle or canula in order to remove fluid or air from the pleural cavity for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes,
Chest drains also known as under water sealed drains UWSD are inserted to allow draining of the pleural spaces of air blood or fluid allowing expansion of the lungs and restoration of negative pressure in the thoracic cavity The underwater seal also prevents backflow of air or fluid into the pleural cavity, Appropriate chest drain management is required to maintain respiratory function
This video breaks down a TMC Practice Question about a Chest Tube Pleural Drainage System,? TMC Test Bank All Practice Questions ? http://bit,ly/2IGeqS
Management of Large Pleural Effusion/Chest tube Management
· Fichier PDF
The pleurodesis will be done through the tube chest drain that has already been put into your chest to drain away the fluid or air that has collected in your pleural space, Once the fluid has drained completely, the doctor will arrange a chest X-ray, The doctor will also do an ultrasound scan a procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image , 2 of 4 of part of the inside