voltage definition electricity – electrical voltage chart
In every case, measuring voltage electrical, EMF, or potential difference represents the fact that current flows between two points if a conductive path is provided, The number of charge carriers might be small even if the voltage is huge, or very large even if the voltage is tiny, Voltage dropped represents the pressure or driving force that impels the charge to move, In general, for a given
What is Voltage » Electronics Notes
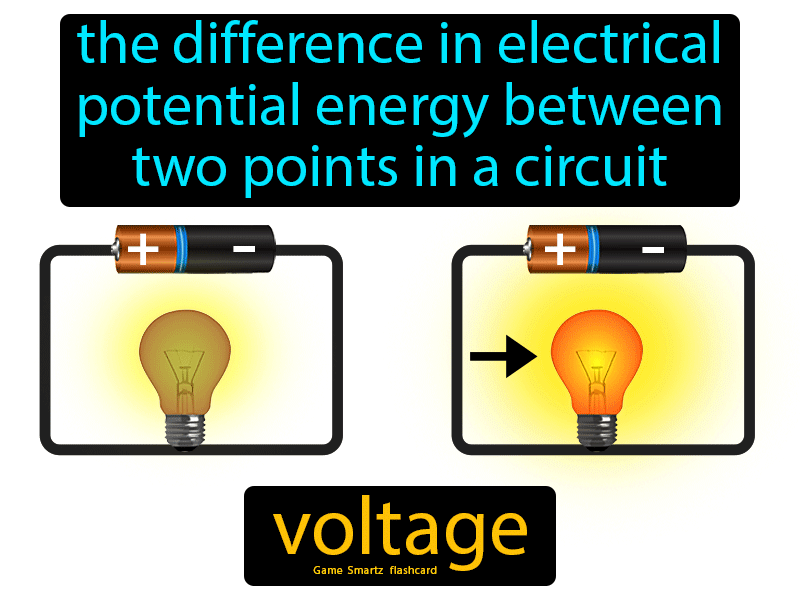
· Voltage is a representation of the electric potential energy per unit charge, If a unit of electrical charge were placed in a location, the voltage indicates the potential energy of it at that point,
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 3 mins
What is Voltage? Electric Potential Difference and EMF
· Voltage explained, What is voltage and what does it do? In this video we discuss how it work and its purpose to understand how electricity works, We’ll look
Auteur : The Engineering Mindset
Découvrez les principales unités de mesure de l’électricité ! Le volt, ou la tension électrique, Le volt V est l’unité de mesure de la tension électrique dans un circuit entre un point A et un point B, obtenue avec un appareil appelé voltmètre, C’est à Alessandro Volta, physicien italien …
· Définition Electricity is produced at voltages of around 15,000 volts, Uses in industry and in certain service sectors require high voltages, while certain uses in …
Voltage is the difference in charge between two points, Current is the rate at which charge is flowing, Resistance is a material’s tendency to resist the flow of charge current,
· The voltage is the electric potential between two points; the greater the voltage the greater will be the current flow through that point It is denoted by letter V or E used for representing electromotive force Voltage is also known as Electric Pressure Electric Tension or Electric Potential Difference,
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 10 mins
Volt, watt, ampère : les unités en électricité
What is Voltage?
Voltage basics Voltage can be considered as the pressure that forces the charged electrons to flow in an electrical circuit This flow of electrons is the electrical current that flows Voltage shown within a simple circuit,
· The voltage is equivalent to the water pressure, the current is equivalent to the flow rate, and the resistance is like the pipe size, There is a basic equation in electrical engineering that states how the three terms relate, It says that the current is equal to the voltage divided by …
Tension électrique — Wikipédia
Voltage Meaning
What are amps, watts, volts and ohms?
Voltage
Voltage is the rate at which energy, electricity or electromagnetic forces are drawn from a source, The specific amount of electricity available in a circuit is an example of voltage, noun
Voltage Definition in Physics
La notion de tension électrique est aussi désignée par l’anglicisme : « voltage » comme il est possible de trouver l’expression « ampérage » pour désigner l’intensité électrique Cependant ces termes sont considérés comme incorrects même si certains les considèrent équivalents [3] [4] [5]
Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm’s Law
Voltage Explained
Definition
Definition, There are multiple useful ways to define voltage, including the standard definition mentioned earlier, There are also other useful definitions of work per charge see this section,, Voltage is defined so that negatively charged objects are pulled towards higher voltages, while positively charged objects are pulled towards lower voltages,
· Voltage is the pressure from an electrical circuit’s power source that pushes charged electrons current through a conducting loop, enabling them to do work such as illuminating a light, In brief, voltage = pressure , and it is measured in volts V,
Temps de Lecture Estimé: 4 mins
What is Voltage?
voltage definition electricity